Your warehouse staff complains about hot spots near the loading dock while your office workers bundle up near the AC vents. This common scenario in large facilities isn’t just uncomfortable—it’s costing you thousands in wasted energy. Commercial ceiling fan installation solves these problems by creating uniform temperatures across expansive spaces, but only when done correctly. Unlike residential installations that take an afternoon, commercial projects require specialized expertise to handle large-scale equipment, complex electrical systems, and structural considerations. This guide reveals the critical steps you must follow for successful commercial ceiling fan installation that delivers maximum comfort, energy savings, and safety in warehouses, retail spaces, and industrial facilities.
Commercial ceiling fans move dramatically more air than residential models—often 50,000+ CFM compared to 5,000-10,000 CFM in homes. This capacity difference means installation isn’t just about mounting a larger fan; it demands structural reinforcement, electrical upgrades, and precise airflow planning. When properly installed, commercial ceiling fans reduce HVAC energy consumption by up to 30% while extending equipment lifespan. In this guide, you’ll learn exactly how to select, install, and optimize commercial ceiling fans for your specific facility needs.
Why Residential Fan Installations Fail in Commercial Spaces
Commercial ceiling fan installation requires fundamentally different approaches than residential projects. Attempting to install residential-grade fans in large facilities creates immediate performance issues and long-term safety hazards.
Commercial fans weigh significantly more—HVLS models can exceed 200 pounds—demanding structural mounting points that residential installations ignore. Standard ceiling joists supporting residential fans often can’t handle commercial unit weight combined with rotational forces. Installers must locate and reinforce structural elements like roof trusses or add dedicated mounting plates rated for dynamic loads.
Electrical requirements differ substantially. Commercial fans often need 208-240V circuits with dedicated breakers, while residential units typically run on standard 120V circuits. HVLS fans with Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) introduce additional electrical complexities including harmonic distortion that requires filtering to prevent interference with other equipment.
Blade design and motor engineering create operational differences. Commercial fans use steeper blade pitches (typically 12-14 degrees) optimized for moving massive air volumes across large spaces. Their industrial-grade motors feature sealed bearings and thermal protection for continuous 24/7 operation—a critical consideration for facilities running multiple shifts.
How to Choose & Size Commercial Ceiling Fans for Your Facility

Selecting the right commercial ceiling fan prevents costly rework and ensures optimal performance from your installation investment. Follow these specific sizing guidelines based on your facility characteristics.
Determine Blade Span Based on Ceiling Height and Square Footage
HVLS fans require specific height-to-blade span ratios for effective air movement. For ceilings 20-30 feet high (common in warehouses), use 8-14 foot diameter fans. Facilities with 30-50 foot ceilings need 14-24 foot fans for proper air displacement. Measure your square footage and divide by the fan’s coverage area (typically 22,000 sq ft per fan for 24-foot models) to determine quantity.
Match Motor Power to Your Environmental Conditions
Industrial environments demand motors with specific protection ratings:
– NEMA 4X rating for washdown areas
– Explosion-proof motors for chemical facilities
– Corrosion-resistant coatings for high-humidity spaces
Verify that your electrical infrastructure supports the motor’s full load amperage plus 25% headroom for startup surges. HVLS fans with VFDs require additional electrical planning to address harmonic distortion.
Certified Commercial Ceiling Fan Installation Prevents Safety Hazards

HVLS fan installation demands manufacturer-certified technicians—this isn’t optional for facility safety. Improperly installed commercial ceiling fans create serious risks:
- Structural failure from inadequate mounting (fans can weigh 200+ pounds)
- Electrical hazards from improper wiring of high-voltage systems
- Falling components from vibration-induced fastener loosening
Top manufacturers like Big Ass Fans require installers to complete rigorous certification programs covering:
– Structural mounting protocols for various building types
– Electrical safety standards for commercial power systems
– Load calculation methods for dynamic rotational forces
– Fall protection requirements for elevated installations
Verify installer credentials by requesting proof of current manufacturer certification and checking their insurance coverage for commercial installations. Never proceed without documentation showing certification specific to the fan model you’re installing.
7 Critical Pre-Installation Checks for Commercial Projects
Skip these steps and your commercial ceiling fan installation will face delays, safety issues, or performance failures.
Conduct Airflow Mapping Before Mounting
Identify optimal fan placement by analyzing:
– Building layout and obstruction locations (racking, machinery)
– Existing HVAC airflow patterns
– Problem areas with temperature stratification
– Employee work zones requiring focused comfort
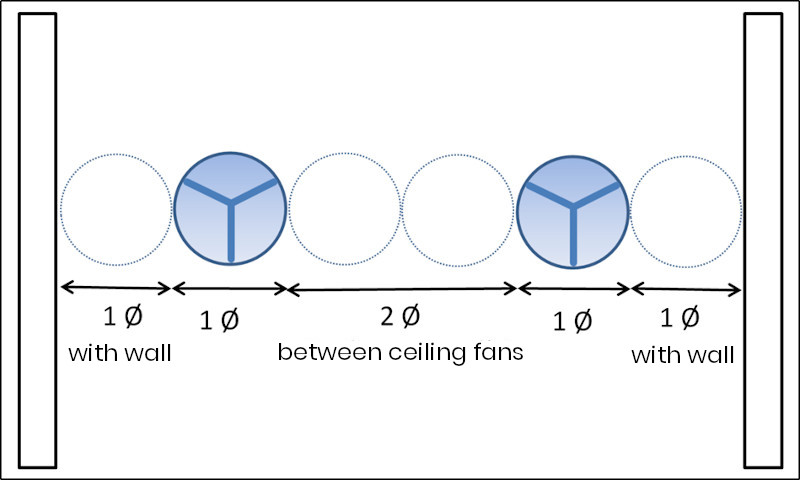
HVLS fans perform best in open areas with minimal obstructions—position them where air can move freely downward and outward. Avoid mounting within 10 feet of walls or large equipment.
Verify Structural Mounting Capacity
Use a stud finder to locate structural elements capable of supporting dynamic loads. Commercial fans require mounting to:
– Roof trusses (not just ceiling joists)
– Steel purlins in metal buildings
– Reinforced concrete structures
When structural elements don’t align with optimal airflow positions, install steel mounting plates spanning between supports. Torque all fasteners to manufacturer specifications—typically 45-60 ft-lbs for commercial applications.
Step-by-Step Commercial Ceiling Fan Installation Process
Follow this sequence for safe, effective installation of commercial ceiling fans in large facilities.
Mounting System Installation Protocol
- Mark mounting points based on airflow mapping
- Locate and verify structural elements with stud finder
- Install mounting plate using grade 8 bolts torqued to 50 ft-lbs
- Attach fan mount to plate with vibration-dampening hardware
- Double-check level and alignment before proceeding
VFD and Electrical Connection Procedure
- Install VFD in accessible, ventilated location per manufacturer specs
- Run dedicated circuit from electrical panel with appropriate gauge wire
- Connect power supply to VFD inputs following wiring diagram
- Program motor parameters using nameplate data
- Test operation at low speed before full activation
VFD Installation Cuts Commercial Fan Energy Costs by 50%

Variable Frequency Drives are essential for maximizing ROI from commercial ceiling fan installation. Proper VFD setup delivers dramatic energy savings through:
- Soft-start capability reducing electrical stress during startup
- Precise speed control matching airflow to actual conditions
- Cubic energy savings relationship (50% speed reduction = 87.5% energy reduction)
Configure VFDs to operate fans at 60-70% speed during normal conditions—this provides adequate airflow while minimizing energy consumption. Program seasonal adjustments that automatically reduce winter speeds to circulate warm air without creating drafts.
Commercial Ceiling Fan Maintenance Checklist
Schedule these maintenance tasks to prevent downtime and extend equipment life:
Monthly:
– Inspect blade balance and alignment
– Check for unusual vibration or noise
– Verify secure mounting hardware
Quarterly:
– Clean blades with non-abrasive cleaner
– Inspect electrical connections for corrosion
– Test emergency stop functions
Annually:
– Perform full torque check on all fasteners
– Verify motor temperature during operation
– Calibrate VFD parameters against baseline
Maximizing ROI: Commercial Fan Speed Settings for Every Season
Optimize your commercial ceiling fan installation with these seasonal adjustments:
- Summer: Run fans at 70-80% speed with downward airflow (forward rotation) to enhance evaporative cooling
- Winter: Reduce to 30-40% speed with upward airflow (reverse rotation) to gently circulate warm air
- Shoulder Seasons: Use demand-based control with occupancy sensors to operate only when spaces are occupied
HVLS fans in warehouses should run continuously at reduced speeds rather than cycling on/off—this maintains consistent temperatures while using less energy than startup surges from frequent cycling.
Commercial Ceiling Fan Installation Cost vs. Energy Savings Breakdown
A typical 20,000 sq ft warehouse installation with two 24-foot HVLS fans costs $12,000-$18,000 including equipment and professional installation. The return comes quickly:
- 25-35% reduction in HVAC energy consumption
- $1,500-$2,500 annual savings on a $6,000 cooling bill
- HVAC equipment lifespan extended by 25-40%
Most commercial ceiling fan installations achieve full payback within 2-3 years through energy savings alone—before accounting for productivity gains from improved worker comfort.
Commercial ceiling fan installation transforms large facilities into more comfortable, efficient spaces when done correctly. Focus on certified installation, proper sizing, and strategic placement to maximize your investment. Start with a professional airflow assessment, choose manufacturer-certified installers, and implement a maintenance schedule to ensure your fans deliver decades of reliable service. The most successful installations treat fans as integrated components of your building’s environmental system—not standalone devices—coordinating them with HVAC operation for maximum comfort and energy savings.