You’re relaxing in your living room when you suddenly wonder: just how fast is that ceiling fan rotating above you? Most homeowners have asked this question while feeling the breeze from their overhead fan. Understanding ceiling fan speed isn’t just curiosity—it directly impacts your comfort, energy efficiency, and even your electricity bill. Ceiling fans don’t spin at a single fixed rate; their rotation speed varies significantly based on multiple factors including fan size, motor type, and selected settings. Knowing the typical revolutions per minute (RPM) ranges helps you optimize airflow for summer cooling or winter heat distribution. This guide reveals the actual speed ranges you can expect from your ceiling fan across different settings, explains what influences these speeds, and shows how to maximize performance for your specific space.
Standard Ceiling Fan Speed Ranges by Setting
Ceiling fans operate across multiple speed settings that dramatically affect their rotation rate and airflow performance. Understanding these standard ranges helps you select appropriate speeds for different conditions.
Low Setting: Gentle Airflow Without the Draft
On low speed, most residential ceiling fans rotate between 50-100 RPM, creating a subtle breeze perfect for mild temperatures or sleeping. This slower rotation moves enough air to create a cooling effect without generating uncomfortable drafts. You’ll typically hear minimal motor noise at this setting, making it ideal for bedrooms or quiet spaces. The blades appear to move slowly enough that you can easily track their motion with your eyes. During cooler months, running your fan clockwise at this low speed gently pushes warm air down from the ceiling without creating a chilling effect.
Medium Setting: Balanced Cooling Performance
At medium speed, ceiling fans generally operate between 100-150 RPM, striking the optimal balance between airflow and energy consumption for most living spaces. This setting provides noticeable cooling without excessive noise, making it the most commonly used speed during warm weather. The blades move quickly enough that individual rotations blur together, but you can still distinguish the blades as they pass fixed points. Most homeowners find this setting effective for maintaining comfort while keeping energy costs reasonable—typically consuming 15-35 watts depending on fan size and motor efficiency.
High Setting: Maximum Air Circulation
When set to high, standard ceiling fans reach their peak performance between 150-250 RPM, depending on blade design and motor power. This maximum speed creates substantial airflow that can significantly enhance evaporative cooling on hot days. The blades become nearly invisible as they rotate, creating a continuous disc-like appearance. While this setting provides the strongest breeze, it also generates the most motor noise and consumes the most energy (usually 30-75 watts). High speed works best for quickly cooling a room or during periods of extreme heat, but shouldn’t be used continuously as it can create uncomfortable drafts and unnecessary energy expenditure.
Factors That Determine Ceiling Fan Rotation Speed

Multiple design and operational elements influence how fast your ceiling fan spins under various conditions. Recognizing these factors helps you understand why different fans perform uniquely in similar spaces.
Blade Design and Pitch Angle Impact
The number of blades and their pitch angle significantly affect rotation speed and airflow efficiency. Fans with fewer blades (3-4) typically spin faster than those with more blades (5+) to move equivalent air volume. The blade pitch—the angle at which blades are set—determines how much air gets pushed with each rotation. Higher pitch angles (12-15 degrees) create more downward airflow at lower RPMs, while flatter blades require higher rotation speeds to achieve similar cooling effects. Modern energy-efficient fans often use optimized blade designs that maximize airflow at lower RPMs, reducing both energy consumption and noise.
Motor Type and Power Specifications
The motor represents the heart of your ceiling fan’s speed capabilities. Traditional AC induction motors operate at fixed speed ranges determined by the number of windings, while newer DC motor fans offer much wider speed variability through electronic controls. Standard AC motors typically deliver three distinct speed settings with limited range between them, whereas DC motor fans provide smoother transitions across a broader RPM spectrum. Higher quality motors maintain consistent speed regardless of minor voltage fluctuations, while cheaper models may slow down as electrical load increases in your home.
Ceiling Height and Room Size Considerations
Your ceiling height directly influences optimal fan speed selection. In rooms with standard 8-9 foot ceilings, medium to high speeds work best to push air down effectively. For vaulted or high ceilings (10+ feet), running your fan at higher RPMs becomes necessary to ensure airflow reaches the living space. Larger rooms require faster rotation speeds to circulate air throughout the entire space, while smaller rooms might achieve sufficient airflow at lower settings. Fans installed in open floor plans often need higher operating speeds to compensate for the larger air volume they must move.
Measuring and Adjusting Your Ceiling Fan Speed
Knowing how to assess and modify your fan’s rotation rate ensures you’re getting optimal performance from your specific model and installation.
Using Smartphone Apps to Measure RPM
You don’t need specialized equipment to determine your ceiling fan’s actual speed. Free smartphone apps like “Phyphox” or “AndroSensor” use your phone’s camera and light sensor to calculate RPM through stroboscopic analysis. Simply point your phone’s camera at the rotating fan (from a safe distance), activate the app’s RPM measurement function, and let the software analyze the rotation rate. This method provides surprisingly accurate readings that help you verify whether your fan is performing within expected parameters or if speed control issues exist.
Addressing Speed Control Problems
If your ceiling fan isn’t reaching expected speeds or behaves erratically across settings, several common issues could be responsible. Worn pull-chain switches often cause inconsistent speed performance, particularly on older fans. Dimmer switches not designed for ceiling fans can restrict power delivery, preventing the motor from reaching proper RPM. Electronic speed controllers may develop calibration issues over time, requiring replacement. Before assuming motor failure, check for simple fixes like tightening loose blade attachments or cleaning dust buildup that creates imbalance and slows rotation.
Optimizing Ceiling Fan Speed for Seasonal Efficiency
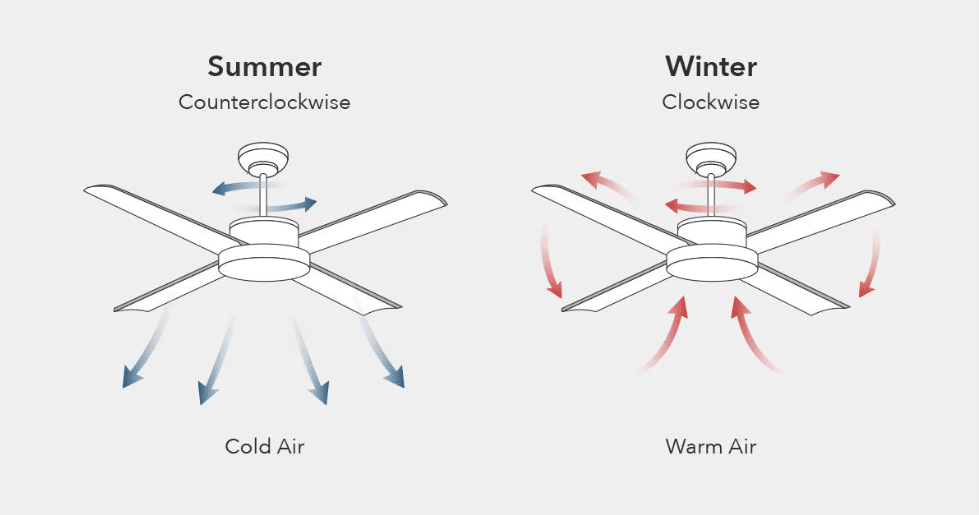
Strategic speed selection throughout the year maximizes both comfort and energy savings from your ceiling fan investment.
Summer Cooling Strategies
During warm months, set your fan to rotate counterclockwise at medium to high speeds (100-250 RPM) to create a strong downward breeze that enhances evaporative cooling on your skin. The wind chill effect allows you to raise your thermostat setting by 4°F while maintaining equivalent comfort, significantly reducing air conditioning costs. In particularly humid conditions where evaporative cooling is less effective, higher speeds become even more important to move sufficient air volume. Remember that ceiling fans cool people, not rooms—always turn them off when spaces are unoccupied to avoid wasting energy.
Winter Heat Distribution Techniques
In colder months, reverse your fan direction to clockwise rotation and operate at low speeds (50-100 RPM) to gently circulate warm air trapped near the ceiling. High speeds during winter create uncomfortable drafts while failing to effectively redistribute heat. The slow rotation pulls cool air up from below while pushing warmer air down along the walls, creating more uniform temperatures throughout the room. This strategic use of ceiling fans can reduce heating costs by up to 15% by allowing you to lower your thermostat without sacrificing comfort.
Safety Considerations for High-Speed Operation

While ceiling fans are generally safe, understanding speed-related safety factors prevents potential issues.
Maximum Safe Operating Speeds
Manufacturers design ceiling fans with specific maximum RPM limits based on blade balance, motor capabilities, and mounting hardware. Exceeding these limits—often through improper speed controller modifications—creates dangerous vibration and potential blade detachment. Most residential fans should never exceed 300 RPM, as higher speeds dramatically increase centrifugal force on blade attachments. If you notice unusual wobbling, especially at higher speeds, immediately reduce the setting and investigate the cause before continuing operation.
Clearance Requirements for Fast-Spinning Blades
The faster your ceiling fan rotates, the more critical proper clearance becomes. Maintain at least 7 feet of clearance between fan blades and the floor, with additional clearance recommended for higher speed settings. For fans operating consistently at high RPM, consider increasing this clearance to 8 feet, particularly in homes with tall occupants. Ensure at least 18 inches of clearance from walls and light fixtures to prevent air turbulence that reduces efficiency and increases noise at higher speeds.
Final Note: Understanding how fast your ceiling fan spins empowers you to optimize home comfort while minimizing energy costs. By matching fan speed to seasonal needs, room characteristics, and personal comfort preferences, you maximize the return on your ceiling fan investment. Remember that most fans operate between 50-250 RPM across their standard settings, with blade design and motor type significantly influencing performance at each speed level. Regular maintenance ensures your fan continues operating at proper speeds, while strategic seasonal adjustments deliver year-round benefits. For optimal results, combine appropriate fan speeds with smart thermostat settings to create the most energy-efficient home environment possible.

Leave a Reply